Milestones to track, success criteria and key stakeholders
This article is part of our CDP series. To read other articles in this series, click here.
Customer Data Platforms are in fashion, but not a trend that will fade away soon. As a pre-packaged, marketer managed system that unifies a company’s customer data to enable use cases such as personalization and contextual marketing, a CDP delivers high value to B2C businesses.
A successful CDP program requires cross-functional team effort where marketing plays a critical role in defining the program objectives and success criteria. Given the nascent stages of the technology, there is little guidance available to businesses investing in a CDP.
This implementation approach note will serve as a handy guide for B2C enterprises looking to ‘buy’ (and not build) a CDP. Read this for our view on build vs. buy.
Broadly, a CDP implementation program has three phases:
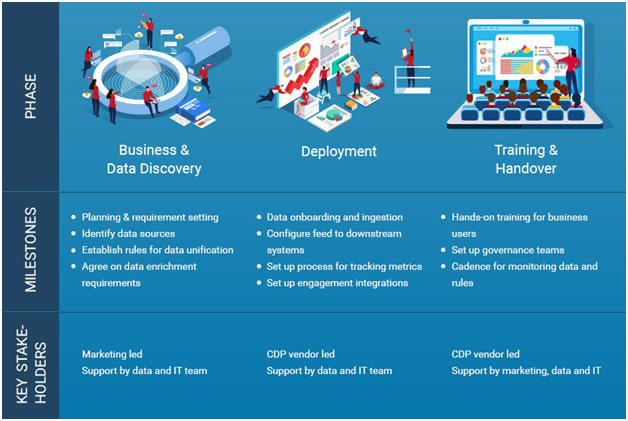
Phase 1: Business and Data Discovery
This phase involves understanding business needs, customer data and the technology landscape – along with buy-in from key stakeholders on how the unified customer record will be created and maintained in the system.
Typical activities include:
-
- Planning and requirement setting
Marketing (CRM/ loyalty and marketing operations) leads this phase where the ask is to define four key program requirements
-
-
-
- Marketing objectives – this could be improving loyalty engagement, customer retention , customer acquisition or customer engagement across touchpoints
- Challenges with current data – is it gaps in the data, poor quality or lack of trust in available data, or a combination of all
- Success criteria – metrics that business will track to validate the quality of customer data against marketing objectives
- Marketing campaigns – the types of campaigns that will be executed once transformed customer data is available, and how the data will be fed to marketing systems such as campaign execution tools
-
- Identify data sources
-
This session is primarily led by data and IT engineering teams who manage customer databases. Marketing technology and analysts may also be involved if they capture customer data via surveys or campaigns. Other aspects covered in this phase require understanding the primary source for customer master, data collection, integration and verification process
-
- Establish business rules for customer data unification
Based on available data and customer marketing priorities, CDP vendors work with marketing and data/ engineering to establish rules for processing and creating a comprehensive view of customer. Some of these rules could be around:
-
-
- Standardization and verification of captured customer data
- Prioritization of data sources for identifying customer attributes, for example, in cases where more than one value/ inconsistent data is present for a given attribute (such as more than one home store for a customer or multiple phone numbers for a customer)
- Establishing mechanism for de-duplicating customer records. This would require agreement on approach to run deterministic and probabilistic matches to create the golden record of a customer
- Customer data enrichment
-
This consists of not only adding customer data from third party sources but also enriching customer data with analytical insights using the ‘as-is’ customer data. Examples of such enrichments are – deriving customer behavior such as a ‘discount buyer’ vs. ‘full price’ buyer – derived from historical purchases and behavior. ‘Active’ visitor or an ‘engaged’ customer based on the customers interactions on e-commerce and digital campaigns. The analytical tags maintained for every customer vary based on marketing objectives, and form critical inputs for segmenting customers to drive engagement. Marketing plays a critical role in identifying data gaps and determine how the data should be enriched.
Phase 2: Deployment
This is where the rubber meets the road. Deployment phase is vendor led (since we are talking buy option) – once critical data (such as customer master) is loaded and processed in the system, marketing is given access to the data. Other customer data activities such as enrichment of ‘nice to have’ customer attributes and cleansing of low priority customers (as defined by business) are executed in an agile manner. This ensures business can use customer data early in the cycle – they can test and validate the results and provide inputs, without having to wait till the end of implementation when it’s too late.
- Data onboarding and ingestion: Getting the process and mechanisms to incorporate data sources and rules agreed upon in Phase 1 in place, to create the comprehensive customer data record
- Configure data feed into downstream marketing systems: This is to ensure marketing teams have access to create customer segments, extract customer lists and data for analytical and personalization purposes
- Set-up process for tracking customer metrics: This stage requires setting up a tracking and measurement process. A critical but often overlooked component of a CDP implementation is to track the health of customer data and business metrics. Information such as total customers vs. active/ inactive customers, customer retention, acquisition and conversion rates are key metrics to track to ensure the program objectives are being met
- (Optional) Set-up customer engagement and campaign integrations: Not all CDPs include ‘engagement features’ – such as real-time interactions or recommendation engines that provide personalized product and offer recommendations to customers using preferred channels such as email, mobile app, online, SMS etc. B2C marketers see higher value from these optional capabilities, making it a prized component of a CDP
Phase 3: Hand over and training
The final phase in a CDP program is to ensure marketing and other customer-facing functions are trained and have access to customer data for their requirements. In addition, data/ engineering teams are trained on monitoring data ingestion and serving from the CDP on an ongoing basis.
The success of a CDP program requires establishing a governance team which comprises of marketing, IT and data engineering. Collectively, they ensure ongoing collection of new data, and verifying/ tweaking the applied rules such that they stay current and continue to meet business needs. By tracking the health of customer data and marketing metrics such as loyalty, acquisition, retention, conversion and engagement consistently, an organization can become truly customer-centric. A well-executed CDP program delivers on business goals quickly, be it controlling customer churn, increasing share of wallet or growing customer value.